arizona's credit repair resource - azscorerestore.com
Credit Score Definition
"A numerical value or a categorization derived from a statistical tool or modeling system used by a person who makes or arranges a loan to predict the likelihood of certain credit behaviors, including default (and the numerical value or the categorization derived from such analysis may also be referred to as a 'risk predictor' or risk score.)" - Source: FACTA
An individual's credit profile is made up from data contained within their credit report from one or more of the major credit bureaus; Experian, Transunion and Equifax.
While there are a couple different credit scoring mechanisms the most popular method in the United States is the FICO (Fair Isaac Corporation) risk score. The purpose of this page is to explain how the FICO credit score works, however it is worth noting a few of the other important credit scores.
Alternatives to FICO Credit Score- Equifax's ScorePower
- Experian's PLUS score
- TransUnion's credit score
- VantageScore credit score
FICO Credit Score
How FICO Score is Calculated
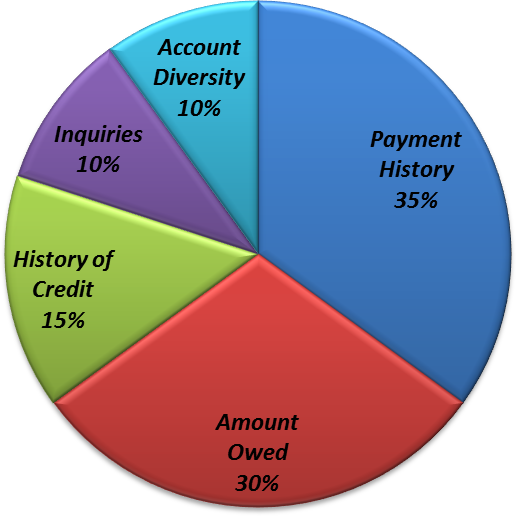
Even though FICO is a public company traded on the New York Stock Exchange, they do not have to divulge the exact formula for how the FICO score is determined. They have however provided guidelines or general categories for what makes up the FICO credit score. This is best represented as a pie with five (5) parts that make up the whole. Displayed to the right is this pie, with brief descriptions of each category below. For a full explanation of the FICO score see our blog post on the FICO Credit Score.
1.) Payment History (35%)
This portion is affected by timeliness of bill payment. This includes how late the payment
was made and if it is still outstanding. Conditions such as how recent the late payment
was and how often you are late also apply.
2.) Amount Owed (30%)
Balances are the name of the game. The type of account such as credit card or mortgage
will also apply here. Lenders do not want to see high credit card balances or many
accounts with small balances.
3.) History of Credit (15%)
The longer credit has been established the better the score. Using existing
accounts frequently will also help the score.
4.) Inquiries (10%)
There are no good inquires, every time someone inquires it hurts the score.
Factors such as recent activity also play a part.
5.) Account Diversity (10%)
A diverse mix of accounts will help the score, i.e. mortgage, auto, credit card.
Opening many accounts in a short period of time may not be good.
Negative Items
Listed below are some of the items that negatively impact an individual's credit report. These apply to all three credit bureaus and are listed by order of severity.
- Bankruptcies and Judgments
- Foreclosures and Repossessions
- Tax and Civil Liens
- Charge Offs
- Late and Slow Payments
- Inquires
How to Improve or Fix Your Score
On the other side of the coin, methods for improving credit in the short term and over the long run are as follows:
1. Pay bills on time.
(Paying off a collection account does not remove it from the report)
2. Pay off debt, don't move it around.
3. Keep Balances Low on Existing Credit Cards.
(Don't closed unused or open new credit card accounts.)
4. Build credit history and diversity.
(Don't open a lot a new accounts too rapidly.)
5. Rate shop for a loan within a focused period of time.
6. Remove or correct items that are inaccurate or outdated.
(Eliminating negative accounts has the largest impact and fastest
results when it comes to improving your score.)
The last area, namely ensuring accurateness of the credit report and challenging or disputing incorrect items is the fastest method for quickly raising a credit score. Nearly 80% of credit report holders fit into this category. If you think you can benefit from this action call one of our specialists @ 888-586-7099 to get a free consultation and see if you can take advantage of legal credit repair.
Credit Score Categories
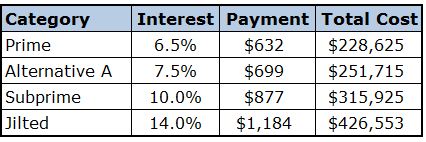
Shown below are the major categories for consumers which are used to group together interest rates. Also displayed below are info-graphics that depict that cost difference between each category over a typical five (5) year auto loan and thirty (30) year mortgage.
- Prime: Scores over 679
- Alt A: Scores between 620 & 679
- Subprime: 500 to 619 Credit Score
- Hard Money (Jilted Bad Credit): Less than 500
Example 1 - $20,0000 auto loan over 5 years
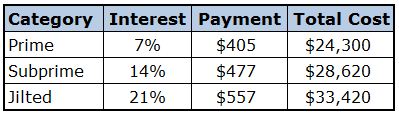
Example 2 - $100,0000 mortgage over 30 years